Cookbook: Langchain Integration
This is a cookbook with examples of the Langfuse Integration for Langchain (Python).
Follow the integration guide to add this integration to your Langchain project. The integration also supports Langchain JS.
Setup
%pip install langfuse langchain langchain_openai langchain_community --upgradeInitialize the Langfuse client with your API keys from the project settings in the Langfuse UI and add them to your environment.
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page
# https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = ""
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = ""
os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
# Your openai key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ""from langfuse.callback import CallbackHandler
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()# Tests the SDK connection with the server
langfuse_handler.auth_check()Examples
Sequential Chain in Langchain Expression Language (LCEL)
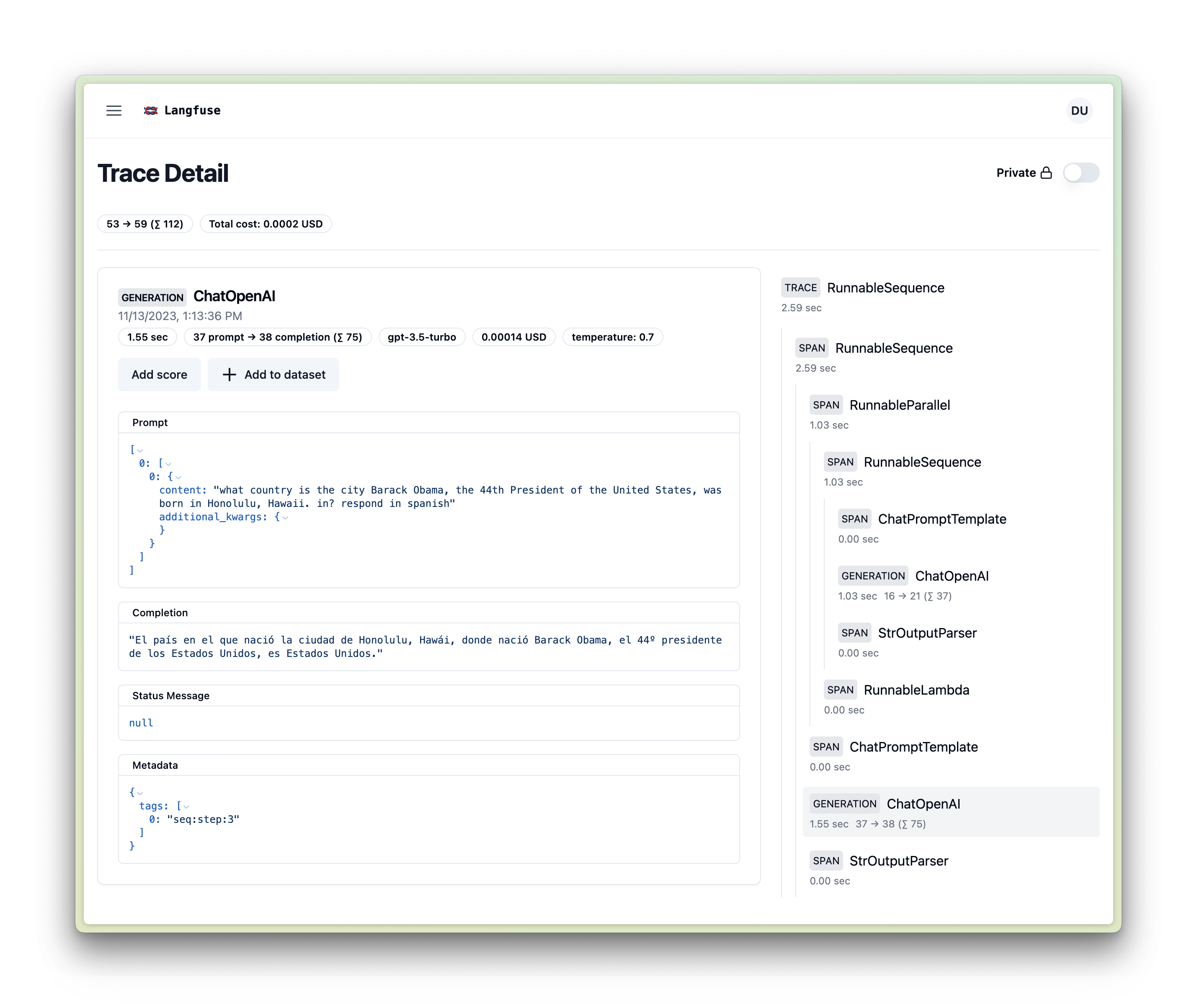
from operator import itemgetter
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.schema import StrOutputParser
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
prompt1 = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("what is the city {person} is from?")
prompt2 = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"what country is the city {city} in? respond in {language}"
)
model = ChatOpenAI()
chain1 = prompt1 | model | StrOutputParser()
chain2 = (
{"city": chain1, "language": itemgetter("language")}
| prompt2
| model
| StrOutputParser()
)
chain2.invoke({"person": "obama", "language": "spanish"}, config={"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]})Runnable methods
Runnables are units of work that can be invoked, batched, streamed, transformed and composed.
The examples below show how to use the following methods with Langfuse:
-
invoke/ainvoke: Transforms a single input into an output.
-
batch/abatch: Efficiently transforms multiple inputs into outputs.
-
stream/astream: Streams output from a single input as it’s produced.
# Async Invoke
await chain2.ainvoke({"person": "biden", "language": "german"}, config={"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]})
# Batch
chain2.batch([{"person": "elon musk", "language": "english"}, {"person": "mark zuckerberg", "language": "english"}], config={"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]})
# Async Batch
await chain2.abatch([{"person": "jeff bezos", "language": "english"}, {"person": "tim cook", "language": "english"}], config={"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]})
# Stream
for chunk in chain2.stream({"person": "steve jobs", "language": "english"}, config={"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]}):
print("Streaming chunk:", chunk)
# Async Stream
async for chunk in chain2.astream({"person": "bill gates", "language": "english"}, config={"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]}):
print("Async Streaming chunk:", chunk)
ConversationChain
We’ll use a session in Langfuse to track this conversation with each invocation being a single trace.
In addition to the traces of each run, you also get a conversation view of the entire session:
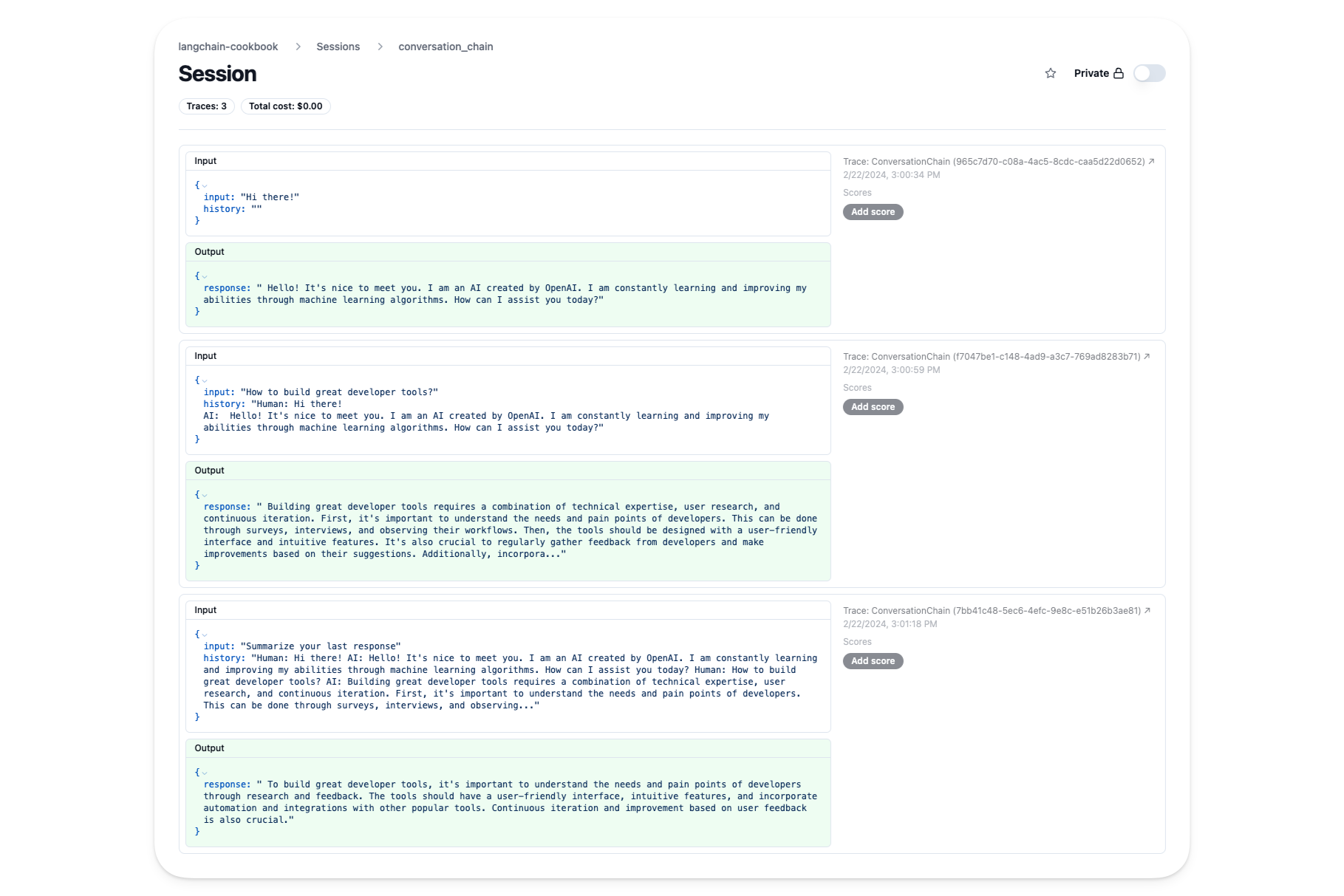
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain_openai import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
conversation = ConversationChain(
llm=llm, memory=ConversationBufferMemory()
)# Create a callback handler with a session
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler(session_id="conversation_chain")conversation.predict(input="Hi there!", callbacks=[langfuse_handler])conversation.predict(input="How to build great developer tools?", callbacks=[langfuse_handler])conversation.predict(input="Summarize your last response", callbacks=[langfuse_handler])RetrievalQA
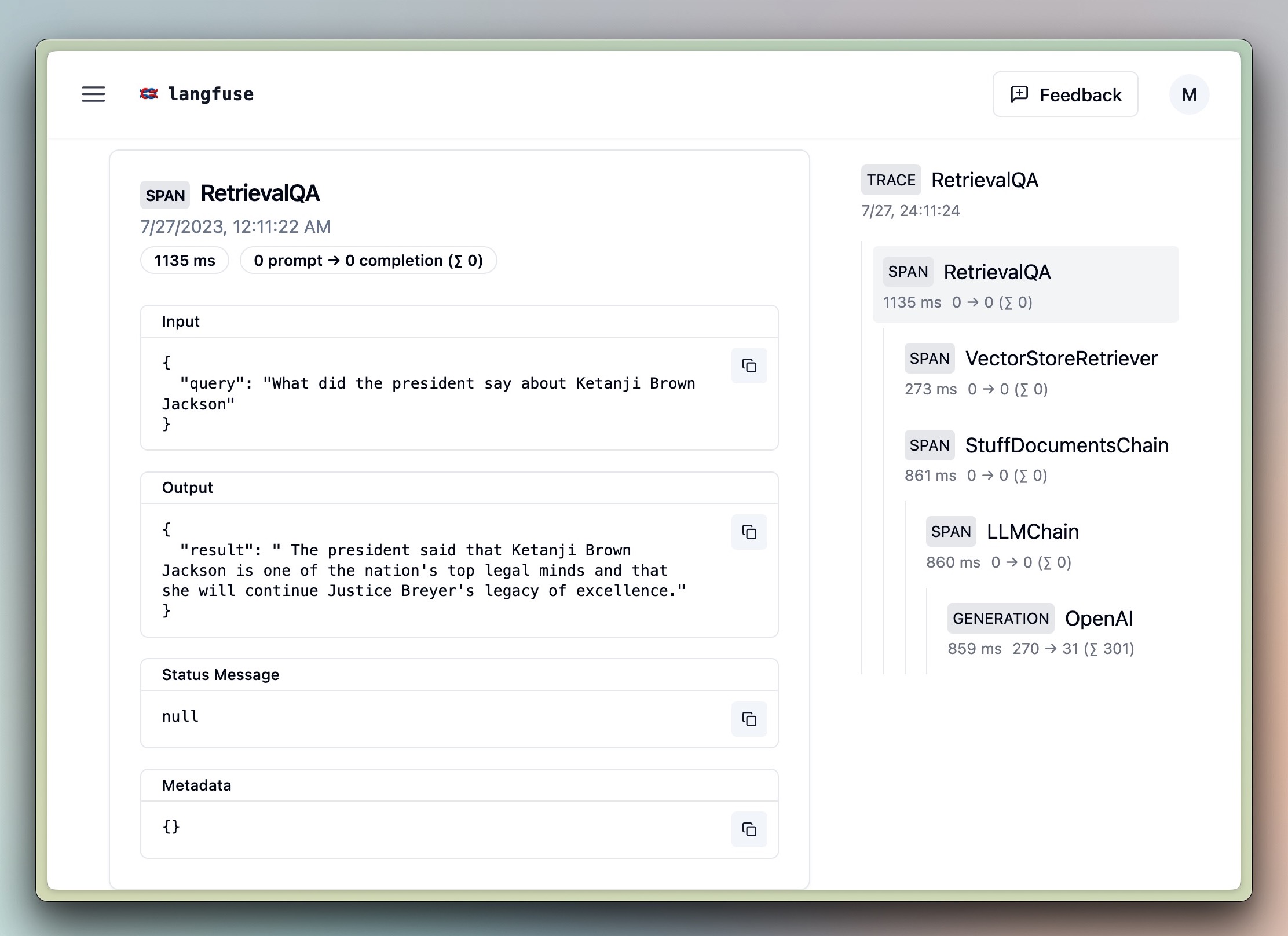
import os
os.environ["SERPAPI_API_KEY"] = ""%pip install unstructured selenium langchain-chroma --upgradefrom langchain_community.document_loaders import SeleniumURLLoader
from langchain_chroma import Chroma
from langchain_text_splitters import CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
urls = [
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/langfuse/langfuse-docs/main/public/state_of_the_union.txt",
]
loader = SeleniumURLLoader(urls=urls)
llm = OpenAI()
documents = loader.load()
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=0)
texts = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
docsearch = Chroma.from_documents(texts, embeddings)
query = "What did the president say about Ketanji Brown Jackson"
chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm,
retriever=docsearch.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 1}),
)
chain.invoke(query, config={"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]})Agent
%pip install google-search-resultsfrom langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, load_tools, create_openai_functions_agent
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain import hub
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
tools = load_tools(["serpapi"])
prompt = hub.pull("hwchase17/openai-functions-agent")
agent = create_openai_functions_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools)
agent_executor.invoke({"input": "What is Langfuse?"}, config={"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]})AzureOpenAI
os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"] = "<Azure OpenAI endpoint>"
os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "<Azure OpenAI API key>"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_TYPE"] = "azure"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_VERSION"] = "2023-09-01-preview"from langchain_openai import AzureChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("what is the city {person} is from?")
model = AzureChatOpenAI(
deployment_name="gpt-35-turbo",
model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo",
)
chain = prompt | model
chain.invoke({"person": "Satya Nadella"}, config={"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]})Sequential Chain [Legacy]
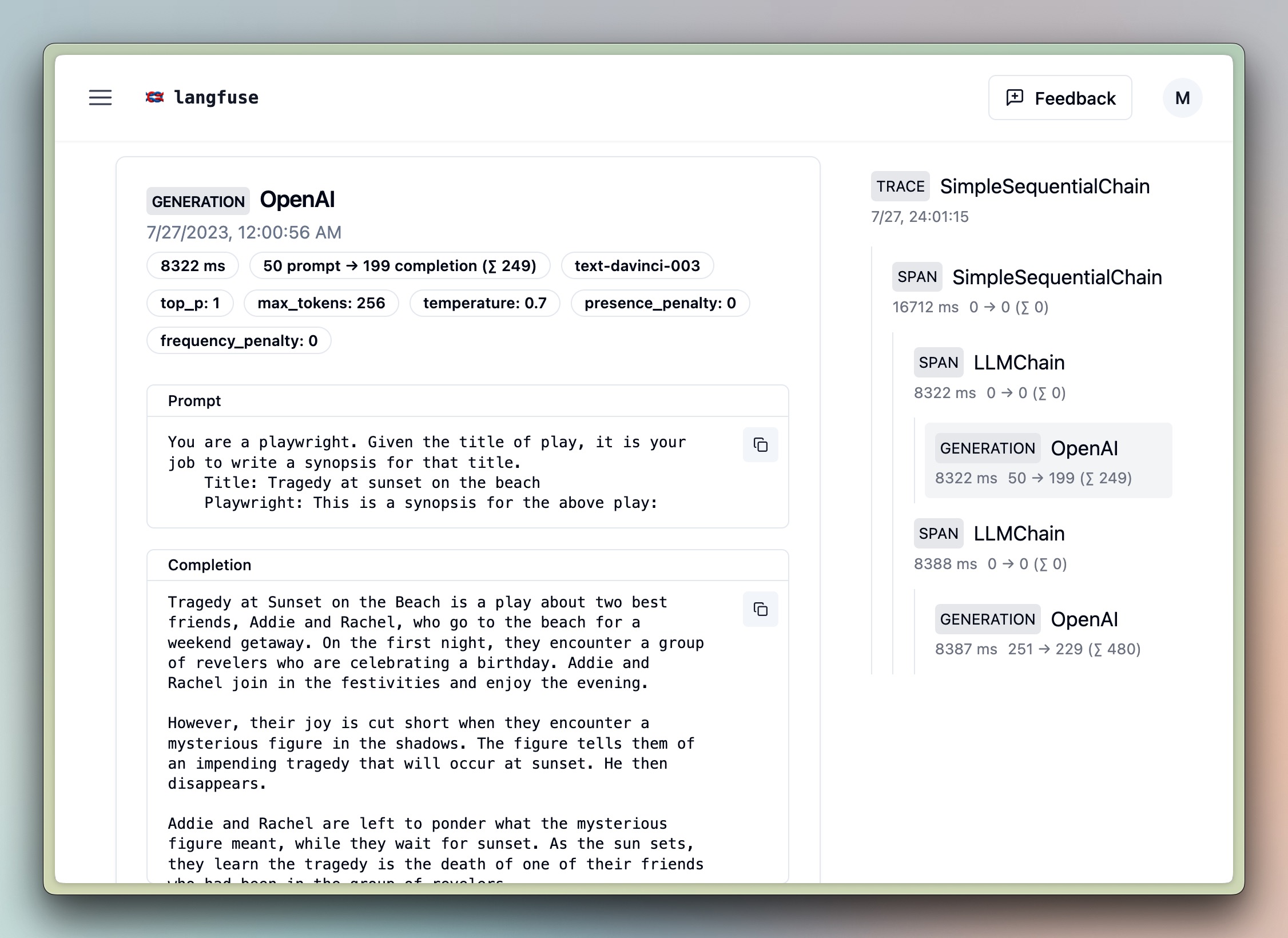
# further imports
from langchain_openai import OpenAI
from langchain.chains import LLMChain, SimpleSequentialChain
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
llm = OpenAI()
template = """You are a playwright. Given the title of play, it is your job to write a synopsis for that title.
Title: {title}
Playwright: This is a synopsis for the above play:"""
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["title"], template=template)
synopsis_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt_template)
template = """You are a play critic from the New York Times. Given the synopsis of play, it is your job to write a review for that play.
Play Synopsis:
{synopsis}
Review from a New York Times play critic of the above play:"""
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["synopsis"], template=template)
review_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt_template)
overall_chain = SimpleSequentialChain(
chains=[synopsis_chain, review_chain],
)
# invoke
review = overall_chain.invoke("Tragedy at sunset on the beach", {"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]}) # add the handler to the run method
# run [LEGACY]
review = overall_chain.run("Tragedy at sunset on the beach", callbacks=[langfuse_handler])# add the handler to the run methodCustomize trace names via run_name
By default, Langfuse uses the Langchain run_name as trace/observation names. For more complex/custom chains, it can be useful to customize the names via own run_names.
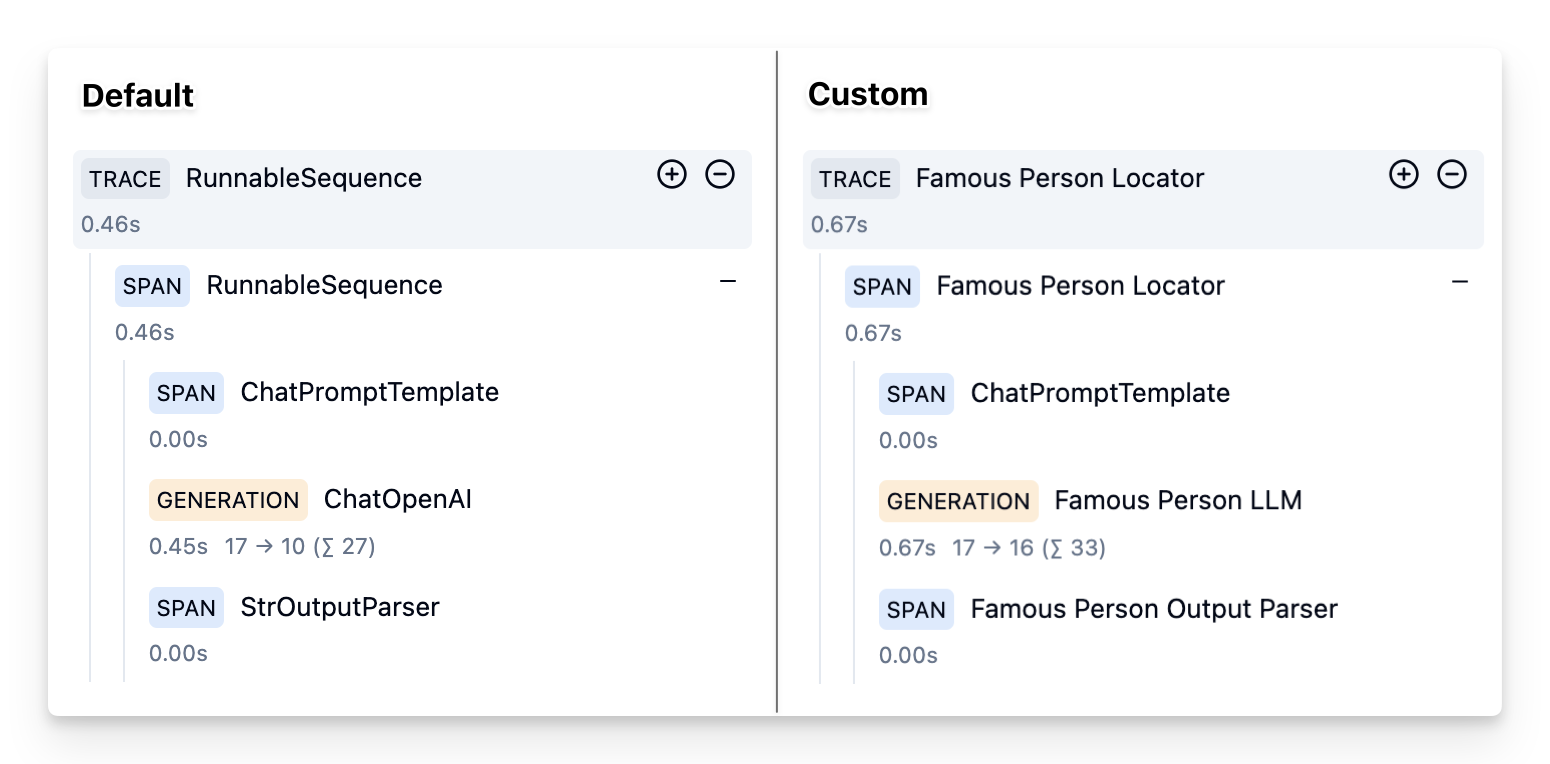
Example without custom run names
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("what is the city {person} is from?")
model = ChatOpenAI()
chain = prompt1 | model | StrOutputParser()
chain.invoke({"person": "Grace Hopper"}, config={
"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]
})Via Runnable Config
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("what is the city {person} is from?").with_config(run_name="Famous Person Prompt")
model = ChatOpenAI().with_config(run_name="Famous Person LLM")
output_parser = StrOutputParser().with_config(run_name="Famous Person Output Parser")
chain = (prompt1 | model | output_parser).with_config(run_name="Famous Person Locator")
chain.invoke({"person": "Grace Hopper"}, config={
"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]
})Example trace: https://cloud.langfuse.com/project/cloramnkj0002jz088vzn1ja4/traces/ec9fcc46-ca38-4bdb-9482-eb06a5f90944
Via Run Config
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("what is the city {person} is from?")
model = ChatOpenAI()
chain = prompt1 | model | StrOutputParser()
chain.invoke({"person": "Grace Hopper"}, config={
"run_name": "Famous Person Locator",
"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]
})Example trace: https://cloud.langfuse.com/project/cloramnkj0002jz088vzn1ja4/traces/b48204e2-fd48-487b-8f66-015e3f10613d
Interoperability with Langfuse Python SDK
You can use this integration in combination with the observe() decorator from the Langfuse Python SDK. Thereby, you can trace non-Langchain code, combine multiple Langchain invocations in a single trace, and use the full functionality of the Langfuse Python SDK.
The langfuse_context.get_current_langchain_handler() method exposes a LangChain callback handler in the context of a trace or span when using decorators. Learn more about Langfuse Tracing here and this functionality here.
How it works
from langfuse.decorators import langfuse_context, observe
# Create a trace via Langfuse decorators and get a Langchain Callback handler for it
@observe() # automtically log function as a trace to Langfuse
def main():
# update trace attributes (e.g, name, session_id, user_id)
langfuse_context.update_current_trace(
name="custom-trace",
session_id="user-1234",
user_id="session-1234",
)
# get the langchain handler for the current trace
langfuse_context.get_current_langchain_handler()
# use the handler to trace langchain runs ...
main()Example
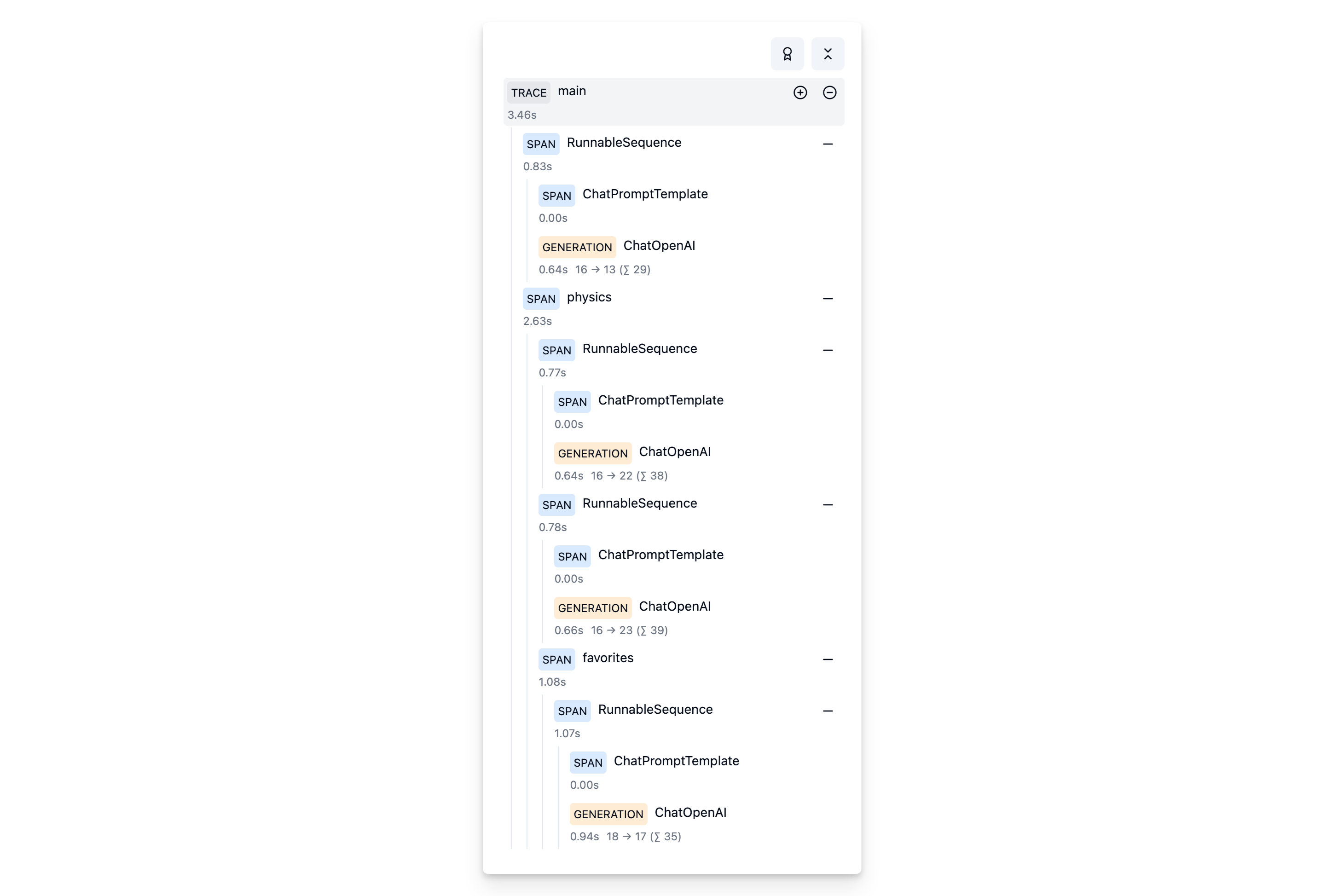
We’ll run the same chain multiple times at different places within the hierarchy of a trace.
TRACE: person-locator
|
|-- SPAN: Chain (Alan Turing)
|
|-- SPAN: Physics
| |
| |-- SPAN: Chain (Albert Einstein)
| |
| |-- SPAN: Chain (Isaac Newton)
| |
| |-- SPAN: Favorites
| | |
| | |-- SPAN: Chain (Richard Feynman)Setup chain
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("what is the city {person} is from?")
model = ChatOpenAI()
chain = prompt | modelInvoke it multiple times as part of a nested trace.
from langfuse.decorators import langfuse_context, observe
# On span "Physics"."Favorites"
@observe() # decorator to automatically log function as sub-span to Langfuse
def favorites():
# get the langchain handler for the current sub-span
langfuse_handler = langfuse_context.get_current_langchain_handler()
# invoke chain with langfuse handler
chain.invoke({"person": "Richard Feynman"},
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]})
# On span "Physics"
@observe() # decorator to automatically log function as span to Langfuse
def physics():
# get the langchain handler for the current span
langfuse_handler = langfuse_context.get_current_langchain_handler()
# invoke chains with langfuse handler
chain.invoke({"person": "Albert Einstein"},
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]})
chain.invoke({"person": "Isaac Newton"},
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]})
favorites()
# On trace
@observe() # decorator to automatically log function as trace to Langfuse
def main():
# get the langchain handler for the current trace
langfuse_handler = langfuse_context.get_current_langchain_handler()
# invoke chain with langfuse handler
chain.invoke({"person": "Alan Turing"},
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]})
physics()
main()View it in Langfuse
Adding evaluation/feedback scores to traces
Evaluation results and user feedback are recorded as scores in Langfuse.
To add a score to a trace, you need to know the trace_id. There are two options to achieve this when using LangChain:
- Provide a predefined LangChain run_id
- Use the Langfuse Decorator to get the trace_id
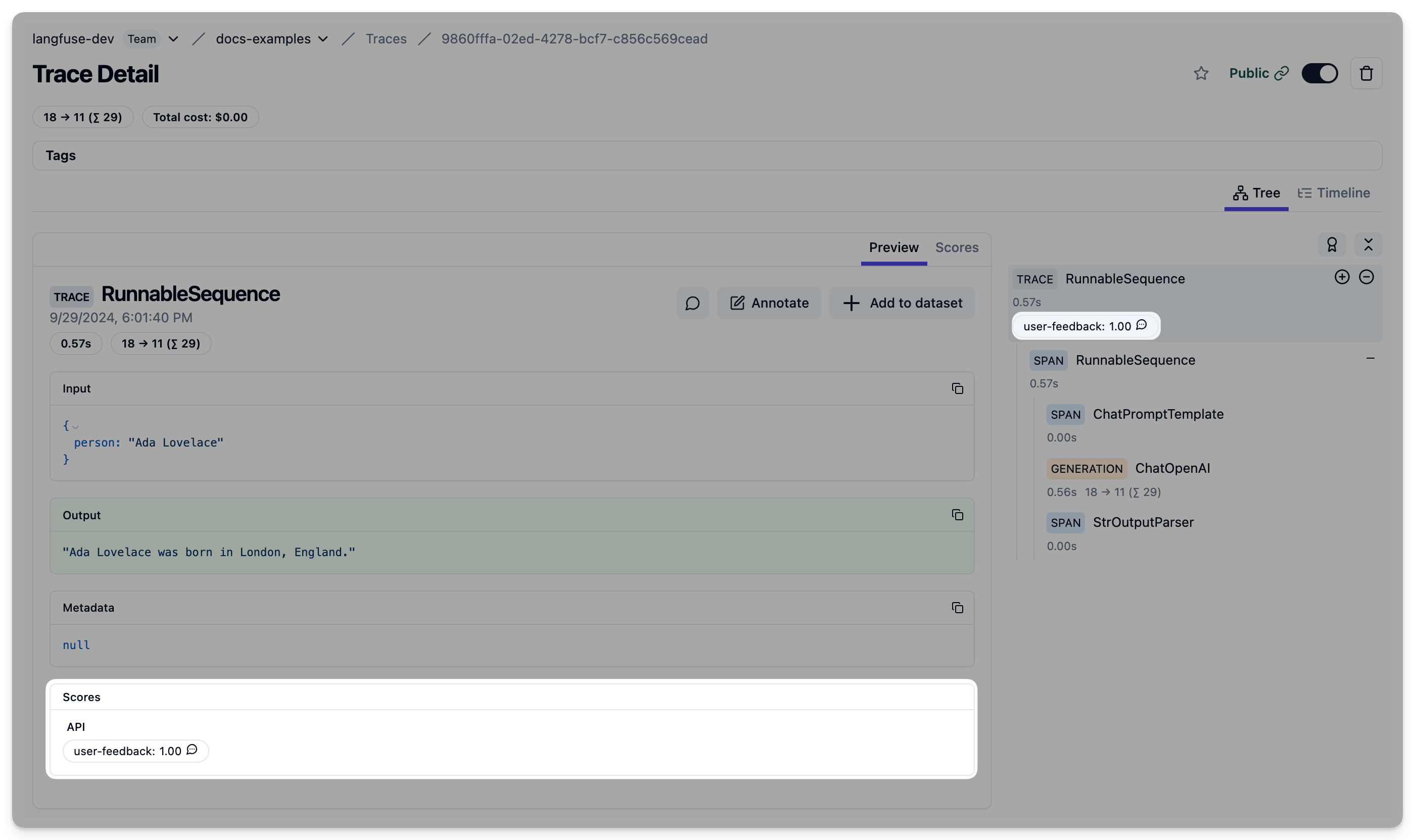
Predefined LangChain run_id
Langfuse uses the LangChain run_id as a trace_id. Thus you can provide a custom run_id to the runnable config in order to later add scores to the trace.
from operator import itemgetter
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.schema import StrOutputParser
import uuid
predefined_run_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("what is the city {person} is from?")
model = ChatOpenAI()
chain = prompt1 | model | StrOutputParser()
chain.invoke({"person": "Ada Lovelace"}, config={
"run_id": predefined_run_id,
"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]
})from langfuse import Langfuse
langfuse = Langfuse()
langfuse.score(
trace_id=predefined_run_id,
name="user-feedback",
value=1,
comment="This was correct, thank you"
);Example Trace in Langfuse: https://cloud.langfuse.com/project/cloramnkj0002jz088vzn1ja4/traces/9860fffa-02ed-4278-bcf7-c856c569cead
Via Langfuse Decorator
Alternatively, you can use the LangChain integration together with the Langfuse @observe-decorator for Python.
from langfuse.decorators import langfuse_context, observe
from operator import itemgetter
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.schema import StrOutputParser
import uuid
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("what is the city {person} is from?")
model = ChatOpenAI()
chain = prompt1 | model | StrOutputParser()
@observe()
def main(person):
langfuse_handler = langfuse_context.get_current_langchain_handler()
response = chain.invoke({"person": person}, config={
"callbacks":[langfuse_handler]
})
trace_id = langfuse_context.get_current_trace_id()
return trace_id, response
trace_id, response = main("Ada Lovelace")from langfuse import Langfuse
langfuse = Langfuse()
langfuse.score(
trace_id=trace_id,
name="user-feedback",
value=1,
comment="This was correct, thank you"
);Example trace: https://cloud.langfuse.com/project/cloramnkj0002jz088vzn1ja4/traces/08bb7cf3-87c6-4a78-a3fc-72af8959a106